G 代码
[TOC]
g
type g struct {
// stackguard0 is the stack pointer compared in the Go stack growth prologue.
// It is stack.lo+StackGuard normally, but can be StackPreempt to trigger a preemption.
// stackguard1 is the stack pointer compared in the C stack growth prologue.
// It is stack.lo+StackGuard on g0 and gsignal stacks.
// It is ~0 on other goroutine stacks, to trigger a call to morestackc (and crash).
// 栈相关的字段
stack stack // 当前 Goroutine 的栈内存范围 [stack.lo, stack.hi)
stackguard0 uintptr // offset known to liblink, 用于调度器抢占式调度, gp.stack.lo + _StackGuard
stackguard1 uintptr // offset known to liblink
_panic *_panic // innermost panic - offset known to liblink
_defer *_defer // innermost defer
m *m // 当前 Goroutine 占用的线程,可能为空;
sched gobuf // 存储 Goroutine 的调度相关的数据,G 切换时,用于保存 G 的上下文
syscallsp uintptr // if status==Gsyscall, syscallsp = sched.sp to use during gc
syscallpc uintptr // if status==Gsyscall, syscallpc = sched.pc to use during gc
stktopsp uintptr // expected sp at top of stack, to check in traceback
param unsafe.Pointer // 用于传递参数,睡眠时其他goroutine可以设置param,唤醒时该goroutine可以获取
atomicstatus uint32 // Goroutine 的状态
stackLock uint32 // sigprof/scang lock; TODO: fold in to atomicstatus
goid int64 // Goroutine 的 ID
schedlink guintptr
waitsince int64 // g被阻塞的大约时间,为什么是大约?
waitreason waitReason // if status==Gwaiting
//与抢占密切相关的字段
preempt bool // 抢占信号, duplicates stackguard0 = stackpreempt
preemptStop bool // 抢占时将状态修改成 `_Gpreempted`; otherwise, just deschedule
preemptShrink bool // 在同步安全点收缩栈
// asyncSafePoint is set if g is stopped at an asynchronous
// safe point. This means there are frames on the stack
// without precise pointer information.
asyncSafePoint bool
paniconfault bool // panic (instead of crash) on unexpected fault address
gcscandone bool // g has scanned stack; protected by _Gscan bit in status
throwsplit bool // must not split stack
// activeStackChans indicates that there are unlocked channels
// pointing into this goroutine's stack. If true, stack
// copying needs to acquire channel locks to protect these
// areas of the stack.
activeStackChans bool
// parkingOnChan indicates that the goroutine is about to
// park on a chansend or chanrecv. Used to signal an unsafe point
// for stack shrinking. It's a boolean value, but is updated atomically.
parkingOnChan uint8
raceignore int8 // ignore race detection events
sysblocktraced bool // StartTrace has emitted EvGoInSyscall about this goroutine
sysexitticks int64 // cputicks when syscall has returned (for tracing)
traceseq uint64 // trace event sequencer
tracelastp puintptr // last P emitted an event for this goroutine
lockedm muintptr
sig uint32
writebuf []byte
sigcode0 uintptr
sigcode1 uintptr
sigpc uintptr
gopc uintptr // G 的 PC,程序计数器,指 goroutine 的创建者 ?
ancestors *[]ancestorInfo // ancestor information goroutine(s) that created this goroutine (only used if debug.tracebackancestors)
startpc uintptr // pc of goroutine function 任务函数
racectx uintptr
waiting *sudog // sudog structures this g is waiting on (that have a valid elem ptr); in lock order
cgoCtxt []uintptr // cgo traceback context
labels unsafe.Pointer // profiler labels
timer *timer // cached timer for time.Sleep
selectDone uint32 // are we participating in a select and did someone win the race?
// Per-G GC state
// gcAssistBytes is this G's GC assist credit in terms of
// bytes allocated. If this is positive, then the G has credit
// to allocate gcAssistBytes bytes without assisting. If this
// is negative, then the G must correct this by performing
// scan work. We track this in bytes to make it fast to update
// and check for debt in the malloc hot path. The assist ratio
// determines how this corresponds to scan work debt.
gcAssistBytes int64 // 存储了当前 Goroutine gc 辅助标记的对象字节数。
}
g.stack Goroutine 的栈内存,简单的线性区域,地址范围 [stack.lo, stack.hi) ,从高地址位向低地址位增长。
gobuf 调度信息存储
gobuf 存储 Goroutine 的调度相关的数据,
type gobuf struct {
// The offsets of sp, pc, and g are known to (hard-coded in) libmach.
sp uintptr // 栈指针(Stack Pointer),指向栈顶
pc uintptr // 程序计数器(Program Counter) pc 寄存器的作用就是存储程序接下来运行的位置,下次访问的内存地址
g guintptr // 持有 runtime.gobuf 的 Goroutine
ctxt unsafe.Pointer
ret sys.Uintreg // 系统调用的返回值
lr uintptr
bp uintptr // for GOEXPERIMENT=framepointer
}
type g struct {
sched gobuf // 存储 Goroutine 的调度相关的数据,G 切换时,用于保存 G 的上下文
...
}
g.sched 字段用于存放 goroutine 的相关调度信息。在创建 goroutine 是,在 runtime.newproc1 中会设置
func newproc1(fn *funcval, argp unsafe.Pointer, narg int32, callergp *g, callerpc uintptr) *g {
...
newg.sched.pc = funcPC(goexit) + sys.PCQuantum
newg.sched.g = guintptr(unsafe.Pointer(newg))
gostartcallfn(&newg.sched, fn)
...
}
// adjust Gobuf as if it executed a call to fn
// and then did an immediate gosave.
func gostartcallfn(gobuf *gobuf, fv *funcval) {
var fn unsafe.Pointer
if fv != nil {
fn = unsafe.Pointer(fv.fn)
} else {
fn = unsafe.Pointer(funcPC(nilfunc))
}
gostartcall(gobuf, fn, unsafe.Pointer(fv))
}
// adjust Gobuf as if it executed a call to fn with context ctxt
// and then did an immediate gosave.
func gostartcall(buf *gobuf, fn, ctxt unsafe.Pointer) {
sp := buf.sp
if sys.RegSize > sys.PtrSize {
sp -= sys.PtrSize
*(*uintptr)(unsafe.Pointer(sp)) = 0
}
sp -= sys.PtrSize
*(*uintptr)(unsafe.Pointer(sp)) = buf.pc
buf.sp = sp
buf.pc = uintptr(fn)
buf.ctxt = ctxt
}
栈指针 sp 中存储了 runtime.goexit 函数的程序计数器,而 pc 中存储了传入函数的程序计数器。pc 寄存器的作用就是存储程序接下来运行的位置.
程序计数器(Program Counter简称PC):是用于存放下一条指令所在单元的地址的地方,即下一步要访问的内存地址。
newproc() 分配G准备运行
创建 goroutine 等核心逻辑都在 runtime.newproc1 函数中。
- 获取或者创建新的 Goroutine 结构体;调用
runtime.gfget()从处理器 P 的gFree队列中,寻找是否有可用的 G (status == Gdead) 如果没有则从全局调度器的sched.gFree列表中获取runtime.g结构体;再没有则返回空。然后通过runtime.malg函数创建新的结构体,分配_StackMin大小也就是 2KB 的栈空间,然后把新创建的 Goroutine 添加到全局列表runtime.allgs - 将传入的参数移到 Goroutine 的栈上;
- 更新 Goroutine 调度相关的属性,设置栈指针 SP,程序计数器 PC ,并更新其状态到 _Grunnable;
- 将 Goroutine 加入处理器的运行队列;
- 尝试调用
runtime.wakep()唤醒 P 运行 G
func newproc(siz int32, fn *funcval) {
argp := add(unsafe.Pointer(&fn), sys.PtrSize)
gp := getg()
pc := getcallerpc()
systemstack(func() {
newg := newproc1(fn, argp, siz, gp, pc)
_p_ := getg().m.p.ptr()
runqput(_p_, newg, true)
if mainStarted { // 如果主 M 已经启动
wakep()
}
})
}
//go:systemstack
func newproc1(fn *funcval, argp unsafe.Pointer, narg int32, callergp *g, callerpc uintptr) *g {
_g_ := getg()
if fn == nil { // 任务函数如果为nil,则抛出异常
_g_.m.throwing = -1 // do not dump full stacks
throw("go of nil func value")
}
acquirem() // disable preemption because it can be holding p in a local var
siz := narg
siz = (siz + 7) &^ 7
if siz >= _StackMin-4*sys.RegSize-sys.RegSize { // 参数太大则抛出异常
throw("newproc: function arguments too large for new goroutine")
}
_p_ := _g_.m.p.ptr()
newg := gfget(_p_) // 从处理器 P 的 gFree 队列中,寻找是否有可用的 G (status == Gdead)
if newg == nil {
newg = malg(_StackMin) // 没有现成可用的,就新创建一个 G 并分配 2KB 栈空间
casgstatus(newg, _Gidle, _Gdead) // 更新状态 为 _Gdead
allgadd(newg) // 把新创建的 Goroutine 添加到 全局列表 runtime.allgs
}
if newg.stack.hi == 0 {
throw("newproc1: newg missing stack")
}
if readgstatus(newg) != _Gdead { // G 状态一定得是 _Gdead
throw("newproc1: new g is not Gdead")
}
// 参数大小+稍微一点空间
totalSize := 4*sys.RegSize + uintptr(siz) + sys.MinFrameSize // extra space in case of reads slightly beyond frame
totalSize += -totalSize & (sys.SpAlign - 1) // align to spAlign
sp := newg.stack.hi - totalSize // 计算G栈顶sp位置,高位地址见去参数的占用空间
spArg := sp
if usesLR {
// caller's LR
*(*uintptr)(unsafe.Pointer(sp)) = 0
prepGoExitFrame(sp)
spArg += sys.MinFrameSize
}
// 如果有参数
if narg > 0 {
// 将函数的全部参数拷贝到栈上,argp 和 narg 分别是参数的内存空间和大小
memmove(unsafe.Pointer(spArg), argp, uintptr(narg)) //进行字节拷贝
//这是堆栈到堆栈的拷贝。如果启用了写屏障,并且源堆栈是灰色的(目标总是黑色的),那么执行屏障复制。
//我们在memmove之后做这个操作,因为目标堆栈上可能有垃圾。
if writeBarrier.needed && !_g_.m.curg.gcscandone {
f := findfunc(fn.fn)
stkmap := (*stackmap)(funcdata(f, _FUNCDATA_ArgsPointerMaps))
if stkmap.nbit > 0 {
// We're in the prologue, so it's always stack map index 0.
bv := stackmapdata(stkmap, 0)
bulkBarrierBitmap(spArg, spArg, uintptr(bv.n)*sys.PtrSize, 0, bv.bytedata)
}
}
}
// 设置新的 Goroutine 结构体的参数,包括栈指针、程序计数器并更新其状态到 _Grunnable
// 初始化G的gobuf,保存sp,pc,任务函数等
memclrNoHeapPointers(unsafe.Pointer(&newg.sched), unsafe.Sizeof(newg.sched))
newg.sched.sp = sp
newg.stktopsp = sp
// 保存goexit的地址到sched.pc,后面会调节 goexit 作为任务函数返回后执行的地址,goroutine结束后会调用goexit
// funcPC(goexit) 获取 goexit 程序计数器
newg.sched.pc = funcPC(goexit) + sys.PCQuantum // +PCQuantum so that previous instruction is in same function
newg.sched.g = guintptr(unsafe.Pointer(newg))
gostartcallfn(&newg.sched, fn) // 将当前的pc压入栈,保存g的任务函数为pc
newg.gopc = callerpc
newg.ancestors = saveAncestors(callergp)
newg.startpc = fn.fn
if _g_.m.curg != nil {
newg.labels = _g_.m.curg.labels
}
// 判断g的任务函数是不是runtime系统的任务函数,是则sched.ngsys加1
if isSystemGoroutine(newg, false) {
atomic.Xadd(&sched.ngsys, +1)
}
casgstatus(newg, _Gdead, _Grunnable)
if _p_.goidcache == _p_.goidcacheend {
// Sched.goidgen is the last allocated id,
// this batch must be [sched.goidgen+1, sched.goidgen+GoidCacheBatch].
// At startup sched.goidgen=0, so main goroutine receives goid=1.
_p_.goidcache = atomic.Xadd64(&sched.goidgen, _GoidCacheBatch)
_p_.goidcache -= _GoidCacheBatch - 1
_p_.goidcacheend = _p_.goidcache + _GoidCacheBatch
}
newg.goid = int64(_p_.goidcache) // 生成唯一的goid
_p_.goidcache++
if raceenabled {
newg.racectx = racegostart(callerpc)
}
// 如果启动了go trace,记录go create事件
if trace.enabled {
traceGoCreate(newg, newg.startpc)
}
releasem(_g_.m)
return newg
}
newproc1() 根据传入的函数指针,参数创建一个状态为 _Grunnable 的 Groutine;
gfget(_p_) 从处理器 P 的 gFree 队列中,寻找是否有可用的 G (status == Gdead);
funcPC(goexit) 获取 goexit 程序计数器;
gostartcallfn(&newg.sched, fn) 保存G 的任务函数 fn 为 程序计数器 pc;
本地队列 _p_.gFree -->gfget()|
全局队列 sched.gFree -->gfget()|--> newproc --> go func 启动Goroutine
新建G new --> malg()-------->|
globrunqget: 调度器每61次就会 runtime.globrunqget 从全局运行队列查找
runqget:用 runtime.runqget 从 P 本地运行队列查找,
findrunnable:runtime.findrunnable 从本地或者全局的运行队列中获取待执行的 Goroutine;调用 findrunnable 函数会触发工作窃取,从其它的处理器的队列中随机获取一些 Goroutine, 优先级依次为:
- 调用
runtime.runqget从 P 本地运行队列查找,找到则 return; - 调用
runtime.globrunqget从全局运行队列查找,找到则 return; - 调用
runtime.netpoll从网络轮询器中查找,找到则 return; - 通过
runtime.runqsteal函数尝试从其他随机的处理器中窃取待运行的 Goroutine,在该过程中还可能窃取处理器中的计时器;
gfget() 获取 dead G
runtime.gfget() 从处理器 P 的 gFree 队列中,寻找是否有可用的 G (status == Gdead)
从 Goroutine 所在处理器的 gFree 列表获取,如果没有则从全局调度器的 sched.gFree 列表中获取。
如果 gFree 队列有可用可用的 Goroutine,则从队列头部返回一个;否则返回空。
// Get from gfree list.
// If local list is empty, grab a batch from global list.
func gfget(_p_ *p) *g {
retry:
// 如果当前处理器 P 的gFree 队列空的,且全局队列不空
if _p_.gFree.empty() && (!sched.gFree.stack.empty() || !sched.gFree.noStack.empty()) {
lock(&sched.gFree.lock)
// 就从全局队列搬 32 个到当前处理器的 gFree 队列
for _p_.gFree.n < 32 {
// Prefer Gs with stacks.
gp := sched.gFree.stack.pop()
if gp == nil {
gp = sched.gFree.noStack.pop()
if gp == nil {
break
}
}
sched.gFree.n--
_p_.gFree.push(gp)
_p_.gFree.n++
}
unlock(&sched.gFree.lock)
goto retry
}
gp := _p_.gFree.pop()
if gp == nil {
return nil
}
...
}
malg() new G 结构体
创建一个新的 Goroutine ,并通过 runtime.stackalloc 分配足 stacksize 字节栈空间。通过 runtime.malg 创建的 Goroutine 会存储到全局变量 runtime.allgs 中。新创建的 Goroutine 状态为 _Gidle。
func malg(stacksize int32) *g {
newg := new(g)
if stacksize >= 0 {
stacksize = round2(_StackSystem + stacksize)
systemstack(func() {
newg.stack = stackalloc(uint32(stacksize)) // 分配栈空间
})
newg.stackguard0 = newg.stack.lo + _StackGuard // 堆栈保护是一个比堆栈底部高出这么多字节的指针 ?
newg.stackguard1 = ^uintptr(0)
// Clear the bottom word of the stack. We record g
// there on gsignal stack during VDSO on ARM and ARM64.
*(*uintptr)(unsafe.Pointer(newg.stack.lo)) = 0
}
return newg
}
runtime._StackSystem 字段表示一些额外的字节,用来添加到每个堆栈,通常是在保护区域下面,用于特定的操作系统目的,如信号处理。在Windows、Plan 9和iOS上使用,因为它们不使用单独的堆栈。
然后调用 runtime.stackalloc 分配栈内存;
Go 代码分配的最小栈为 _StackMin = 2048B;
runqput() 放入待运行队列
runqput() 尝试把 Goroutine 加到 处理本地运行队列 p.runq, 队列长度为256 如果本地运行队列满了,把 Goroutine 加到全局队列。
当 next 为 false, 将 Goroutine 加入处理器持有的本地运行队列;
如果 next 为 true, 将 Goroutine 设置到处理器的 runnext 上作为下一个处理器执行的任务。
如果本地运行队列已满,则把本地队列中的一部分 Goroutine 和待加入的 Goroutine 通过 runqputslow 添加到调度器持有的全局运行队列上;
type p struct {
// Queue of runnable goroutines. Accessed without lock.
runqhead uint32
runqtail uint32
runq [256]guintptr
...
}
func runqput(_p_ *p, gp *g, next bool) {
if randomizeScheduler && next && fastrand()%2 == 0 {
next = false
}
if next {
retryNext:
oldnext := _p_.runnext
if !_p_.runnext.cas(oldnext, guintptr(unsafe.Pointer(gp))) {
goto retryNext
}
if oldnext == 0 {
return
}
// Kick the old runnext out to the regular run queue.
gp = oldnext.ptr()
}
retry:
h := atomic.LoadAcq(&_p_.runqhead) // load-acquire, synchronize with consumers
t := _p_.runqtail
if t-h < uint32(len(_p_.runq)) {
_p_.runq[t%uint32(len(_p_.runq))].set(gp)
atomic.StoreRel(&_p_.runqtail, t+1) // store-release, makes the item available for consumption
return
}
if runqputslow(_p_, gp, h, t) {
return
}
// the queue is not full, now the put above must succeed
goto retry
}
schedule() 调度器主函数
Go runtime 的调度从runtime.schedule开始, 找到一个可运行的 Goroutine 然后执行。
果当前因 GC 处于 STW 状态, 则调用 runtime.gcstopm 休眠当前的 M。
runtime.schedule 会从3个不同地方查找待执行的 Goroutine。
-
当全局运行队列中有待执行的 Goroutine 时,通过
schedtick每调度61次就用runtime.globrunqget从全局的运行队列中查找 Goroutine; -
调用
runtime.runqget从处理器本地的运行队列中查找待执行的 Goroutine, ; -
如果前两种方法都没有找到 Goroutine,就会通过
runtime.findrunnable进行阻塞地查找 Goroutine;
通过 runtime.execute 函数执行获取的 Goroutine,做好准备工作后,它会通过 runtime.gogo 将 Goroutine 调度到当前线程上。
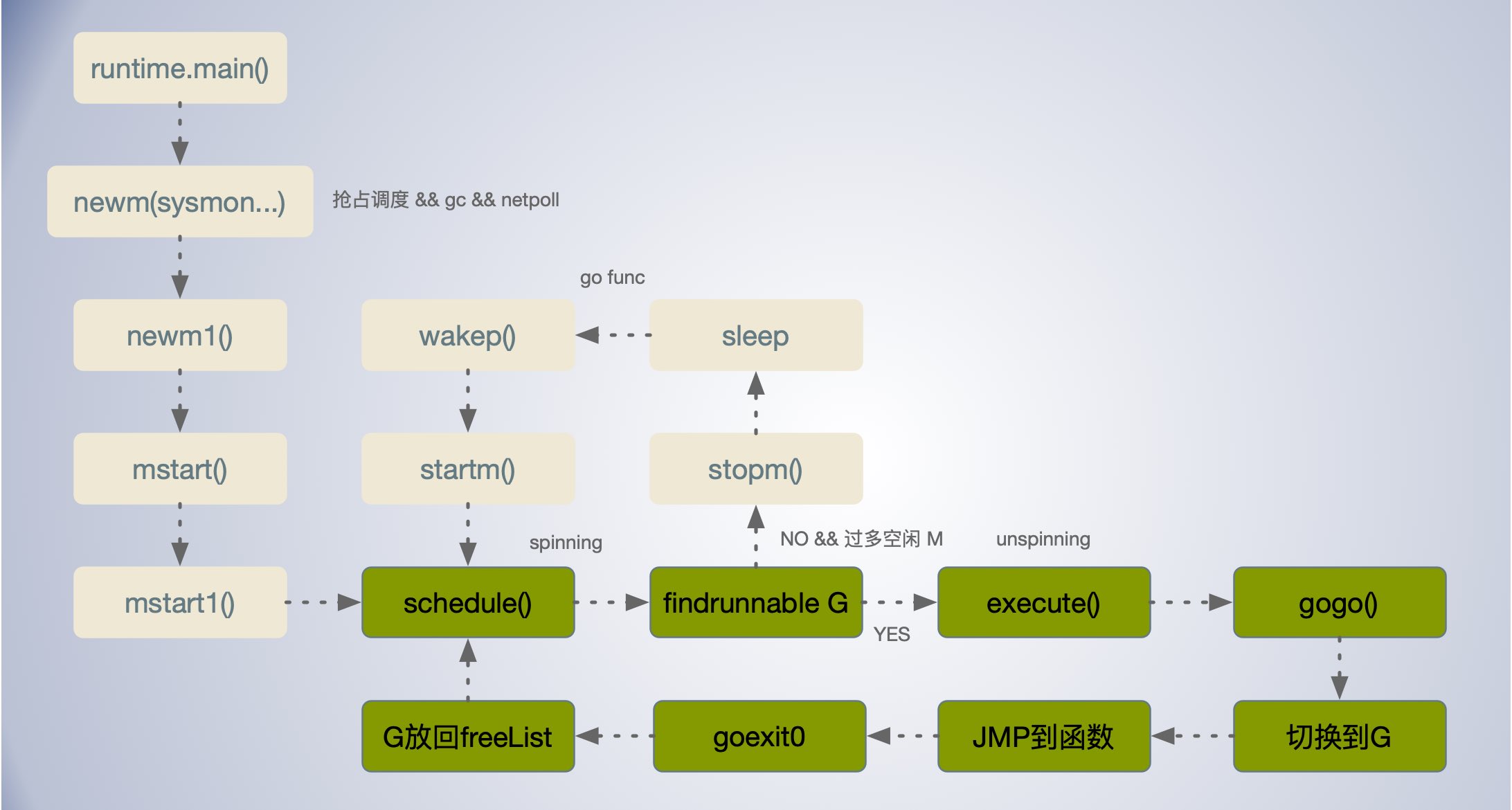
execute() 执行 G 任务函数
通过 runtime.execute 函数执行获取的 Goroutine,做好准备工作后,它会通过 runtime.gogo 将 Goroutine 调度到当前线程M上执行。
如果 inheritTime 为 true 则使用当前的剩余的时间片,否则重开一个时间片。
//go:yeswritebarrierrec
func execute(gp *g, inheritTime bool) {
_g_ := getg()
// 在更新 G 状态为 _Grunning 之前,先分配一个 M
_g_.m.curg = gp
gp.m = _g_.m
casgstatus(gp, _Grunnable, _Grunning) // 更新 goroutine 状态
gp.waitsince = 0 // 被阻塞时间 ?
gp.preempt = false // 不可抢占
// goroutine 中的每次调用都通过将当前的栈指针与 g.stackguard0 进行比较来检查堆栈溢出。
gp.stackguard0 = gp.stack.lo + _StackGuard
if !inheritTime {
_g_.m.p.ptr().schedtick++
}
hz := sched.profilehz
if _g_.m.profilehz != hz {
setThreadCPUProfiler(hz)
}
if trace.enabled {
if gp.syscallsp != 0 && gp.sysblocktraced {
traceGoSysExit(gp.sysexitticks)
}
traceGoStart()
}
gogo(&gp.sched) // 调度并执行,汇编实现
}
// goroutine 中的每次调用都通过将当前的栈指针与gp->stackguard0进行比较来检查堆栈溢出。
// 设置 stackguard0 设为 stackPreempt,导致该 P 中正在执行的G进行下一次函数调用时栈空间检查失败。
gogo()
runtime.gogo 函数可以实现将 Goroutine 调度到当前线程上。通过汇编代码实现
func gogo(buf *gobuf)
函数时,将调用方的返回地址加入栈寄存器 SP 中,然后跳转到目标函数;当目标函数返回后,会从栈中查找调用的地址并跳转回调用方继续执行剩下的代码。
runtime.goexit 的程序计数器被放到了栈 SP 上;
待执行函数的程序计数器被放到了寄存器 BX 上;
// amd64
// func gogo(buf *gobuf)
// restore state from Gobuf; longjmp
TEXT runtime·gogo(SB), NOSPLIT, $16-8
MOVQ buf+0(FP), BX // gobuf 移到 BX 中
MOVQ gobuf_g(BX), DX // gobuf.g 运行的 goroutine 移到 DX
MOVQ 0(DX), CX // 确保 Goroutine 不为空
get_tls(CX) // 从tls 线程本地缓存获取 g 指针
MOVQ DX, g(CX)
MOVQ gobuf_sp(BX), SP // restore SP , 将 runtime.goexit 函数的 PC 放入 栈指针 SP 中
MOVQ gobuf_ret(BX), AX
MOVQ gobuf_ctxt(BX), DX
MOVQ gobuf_bp(BX), BP
MOVQ $0, gobuf_sp(BX) // clear to help garbage collector
MOVQ $0, gobuf_ret(BX) // gobuf.ret
MOVQ $0, gobuf_ctxt(BX) // gobuf.ctxt
MOVQ $0, gobuf_bp(BX)
MOVQ gobuf_pc(BX), BX // 获取待执行函数的程序计数器
JMP BX // 开始执行
Go 函数调用通常会使用 CALL 指令,该指令会将调用方的返回地址加入栈寄存器 SP 中,然后跳转到目标函数;当目标函数返回后,会从栈中查找调用的地址并跳转回调用方继续执行剩下的代码。
MOVL gobuf_sp(BX), SP // 将 runtime.goexit 函数的 PC 恢复到 SP 中
MOVL gobuf_pc(BX), BX // 获取待执行函数的程序计数器
JMP BX // 开始执行
TLS 本地线程存储
每个运行的 Goroutine 的 g 指针保存在当前运行 Goroutine 的系统线程的局部存储 TLS(Thread Local Storage) 中, TLS 类似线程局部存储的地址。
每次调用 get_tls(r),就会将当前的 Goroutine 的地址放到寄存器 r 中。
get_tls 是一个宏函数,在 runtime/go_tls.h 头文件中定义, AMD64平台,get_tls宏函数定义如下:
#ifdef GOARCH_amd64
#define get_tls(r) MOVQ TLS, r
#define g(r) 0(r)(TLS*1)
#endif
get_tls(CX)
MOVQ g(CX), AX //get_tls(CX)之后,g(CX)得到的就是当前的 goroutine 的 g (Move g into AX)
获取g指针
// func getg() unsafe.Pointer
TEXT ·getg(SB), NOSPLIT, $0-8
MOVQ (TLS), AX // TLS类似线程局部存储的地址,地址对应的内存里的数据是g指针
MOVQ AX, ret+0(FP)
RET
获取 goid
如果要获取goid可以先获取 TLS 线程局部存储或g 指针,然后再从 TLS 中获取 g 结构的指针,在根据不同版本 goid 成员的偏移量,就可以从g结构中取出goid。例如:
const g_goid_offset = 152 // Go1.10
func GetGroutineId() int64 {
g := getg()
p := (*int64)(unsafe.Pointer(uintptr(g) + g_goid_offset))
return *p
}
goexit0() 任务结束并重新调度
// goexit continuation on g0.
func goexit0(gp *g) {
_g_ := getg()
casgstatus(gp, _Grunning, _Gdead) // 更新 Goroutine 状态为 _Gdead
if isSystemGoroutine(gp, false) {
atomic.Xadd(&sched.ngsys, -1)
}
// 重制 Goroutine 相关 属性
gp.m = nil
locked := gp.lockedm != 0
gp.lockedm = 0
_g_.m.lockedg = 0
gp.preemptStop = false
gp.paniconfault = false
gp._defer = nil // should be true already but just in case.
gp._panic = nil // non-nil for Goexit during panic. points at stack-allocated data.
gp.writebuf = nil
gp.waitreason = 0
gp.param = nil
gp.labels = nil
gp.timer = nil
if gcBlackenEnabled != 0 && gp.gcAssistBytes > 0 {
// 刷新全局池的辅助信贷。如果应用程序正在快速创建一个退出的goroutines,这将提供更好的节奏信息?
scanCredit := int64(gcController.assistWorkPerByte * float64(gp.gcAssistBytes))
atomic.Xaddint64(&gcController.bgScanCredit, scanCredit)
gp.gcAssistBytes = 0
}
dropg() // 移除 goroutine 与线程 M 的关联
...
gfput(_g_.m.p.ptr(), gp) // 放回处理器的 Goroutine 空闲列表 gFree
...
schedule() // 重新调用 schedule() 触发新的 Goroutine 调度
}
injectglist() 批量放入 runq
injectglist 将列表中的每个可运行对象G添加到某个运行队列中。如果没有当前的P,它们被添加到全局队列中,并且直到npidle M开始运行它们。 否则,对于每个空闲的P,这会向全局队列添加一个G并启动一个m。剩余的G被添加到当前P的本地运行队列中。
func injectglist(glist *gList) {
if glist.empty() {
return
}
...
// 放入运行队列之前,先把所有的 G 状态改为可运行
head := glist.head.ptr()
var tail *g
qsize := 0
for gp := head; gp != nil; gp = gp.schedlink.ptr() {
tail = gp
qsize++
casgstatus(gp, _Gwaiting, _Grunnable)
}
// Turn the gList into a gQueue.
var q gQueue
q.head.set(head)
q.tail.set(tail)
*glist = gList{}
startIdle := func(n int) {
for ; n != 0 && sched.npidle != 0; n-- {
startm(nil, false)
}
}
// 如果当前 M 没有绑定 P,则调用 globrunqputbatch 把 G 添加到 全局列表
pp := getg().m.p.ptr()
if pp == nil {
lock(&sched.lock)
globrunqputbatch(&q, int32(qsize))
unlock(&sched.lock)
startIdle(qsize)
return
}
lock(&sched.lock)
npidle := int(sched.npidle)
var n int
for n = 0; n < npidle && !q.empty(); n++ {
globrunqput(q.pop())
}
unlock(&sched.lock)
startIdle(n)
qsize -= n
// 通过 runqputbatch 批量把 G 添加到 P 本地运行队列。
if !q.empty() {
runqputbatch(pp, &q, qsize)
}
}
runqsteal() 窃取 G
//从p2的本地可运行队列中窃取一半的元素
// p的本地可运行队列。
//返回一个被窃取的元素(如果失败,则返回nil)。
func runqsteal(_p_, p2 *p, stealRunNextG bool) *g {}
gopark() G主动挂起
通过 runtime.gopark 暂停当前 Goroutine ,G 的状态会从 _Grunning 变为 _Gwaiting ,通常是由于不满足运行条件造成等待,如网络IO,通道阻塞等待,waitReason 字段表明来等待的原因。
各种 G 等待原因:
var waitReasonStrings = [...]string{
waitReasonZero: "",
waitReasonGCAssistMarking: "GC assist marking",
waitReasonIOWait: "IO wait",
waitReasonChanReceiveNilChan: "chan receive (nil chan)",
waitReasonChanSendNilChan: "chan send (nil chan)",
waitReasonDumpingHeap: "dumping heap",
waitReasonGarbageCollection: "garbage collection",
waitReasonGarbageCollectionScan: "garbage collection scan",
waitReasonPanicWait: "panicwait",
waitReasonSelect: "select",
waitReasonSelectNoCases: "select (no cases)",
waitReasonGCAssistWait: "GC assist wait",
waitReasonGCSweepWait: "GC sweep wait",
waitReasonGCScavengeWait: "GC scavenge wait",
waitReasonChanReceive: "chan receive",
waitReasonChanSend: "chan send",
waitReasonFinalizerWait: "finalizer wait",
waitReasonForceGCIdle: "force gc (idle)",
waitReasonSemacquire: "semacquire",
waitReasonSleep: "sleep",
waitReasonSyncCondWait: "sync.Cond.Wait",
waitReasonTimerGoroutineIdle: "timer goroutine (idle)",
waitReasonTraceReaderBlocked: "trace reader (blocked)",
waitReasonWaitForGCCycle: "wait for GC cycle",
waitReasonGCWorkerIdle: "GC worker (idle)",
waitReasonPreempted: "preempted",
waitReasonDebugCall: "debug call",
}
func gopark(unlockf func(*g, unsafe.Pointer) bool, lock unsafe.Pointer, reason waitReason, traceEv byte, traceskip int) {
if reason != waitReasonSleep {
checkTimeouts() // timeouts may expire while two goroutines keep the scheduler busy
}
mp := acquirem()
gp := mp.curg
status := readgstatus(gp)
if status != _Grunning && status != _Gscanrunning {
throw("gopark: bad g status")
}
mp.waitlock = lock
mp.waitunlockf = unlockf
gp.waitreason = reason
mp.waittraceev = traceEv
mp.waittraceskip = traceskip
releasem(mp)
// can't do anything that might move the G between Ms here.
mcall(park_m) // 通过 runtime.mcall 在切换到 g0 的栈上调用 runtime.park_m 函数
}
通过 runtime.mcall 在切换到 g0 的栈上调用 runtime.park_m 函数。runtime.mcall 从 g 切换到 g0 堆栈并调用 fn(g),其中 g 是进行调用的 goroutine。mcall 保存 g 的当前 PC/SP 调用栈信息到 g->sched,以便它可以在完成调用后恢复。mcall只能从g栈调用(不能是g0,也不能是gsignal)
runtime.park_m 将当前 Goroutine 的状态从 _Grunning 切换至 _Gwaiting,调用 runtime.dropg 移除 OS 线程 M 和 Goroutine 之间的关联,在这之后就可以调用 runtime.schedule 触发新一轮的调度了。
// park continuation on g0.
func park_m(gp *g) {
_g_ := getg()
if trace.enabled {
traceGoPark(_g_.m.waittraceev, _g_.m.waittraceskip)
}
casgstatus(gp, _Grunning, _Gwaiting)
dropg()
...
schedule()
}
当主动挂起的 Goroutine 运行条件满足后,会通过 runtime.goready 将休眠的 Goroutine 唤醒。
goready() 结束等待标为可运行
把处于 _Gwaiting 的 Goroutine 标记为可运行 _Grunnable。如在 runtime.netpollgoready 和 chan send 中会用到。
func goready(gp *g, traceskip int) {
systemstack(func() {
ready(gp, traceskip, true)
})
}
// Mark gp ready to run.
func ready(gp *g, traceskip int, next bool) {
if trace.enabled {
traceGoUnpark(gp, traceskip)
}
status := readgstatus(gp)
// Mark runnable.
_g_ := getg()
mp := acquirem() // disable preemption because it can be holding p in a local var
if status&^_Gscan != _Gwaiting {
dumpgstatus(gp)
throw("bad g->status in ready")
}
// status is Gwaiting or Gscanwaiting, make Grunnable and put on runq
casgstatus(gp, _Gwaiting, _Grunnable)
runqput(_g_.m.p.ptr(), gp, next)
wakep()
releasem(mp)
}
syscall 系统调用
Go 通过汇编语言 syscall.Syscall 和 syscall.RawSyscall 等方法封装了不同操作系统提供的所有系统调用,其中 syscall.Syscall 的实现如下:
#include "textflag.h"
#include "funcdata.h"
// System calls for 386, Linux
//
#define INVOKE_SYSCALL INT $0x80
TEXT ·Syscall(SB),NOSPLIT,$0-28
CALL runtime·entersyscall(SB) // 调用 runtime.entersyscall 进入系统调用
MOVL trap+0(FP), AX // syscall entry
MOVL a1+4(FP), BX
MOVL a2+8(FP), CX
MOVL a3+12(FP), DX
MOVL $0, SI
MOVL $0, DI
INVOKE_SYSCALL
CMPL AX, $0xfffff001
JLS ok
MOVL $-1, r1+16(FP)
MOVL $0, r2+20(FP)
NEGL AX
MOVL AX, err+24(FP)
CALL runtime·exitsyscall(SB) // 调用 runtime.exitsyscall 退出系统调用
RET
ok:
MOVL AX, r1+16(FP)
MOVL DX, r2+20(FP)
MOVL $0, err+24(FP)
CALL runtime·exitsyscall(SB)
RET
通过汇编指令 INVOKE_SYSCALL 执行系统调用前后,上述函数会调用 runtime.entersyscall 和 runtime.exitsyscall,正是这一层包装能够让我们在陷入系统调用前触发 runtime 的准备和清理工作。
如果本次系统调用不需要 runtime 参与,就会使用 syscall.RawSyscall 简化这一过程,这是处于性能的考虑。
直接进行系统调用会阻塞当前的线程,所以只有可以立刻返回的系统调用才可能会被设置成 RawSyscall 类型,例如:SYS_EPOLL_CREATE、SYS_EPOLL_WAIT(超时时间为 0)、SYS_TIME 等。
entersyscall() 进入系统调用
runtime.reentersyscall 主要会保存当前程序计数器PC和栈位置SP信息,用于调用完恢复,更新 G ,P 为系统调用状态;然后分离 P 和 M 的绑定关系。
runtime.reentersyscall 方法会使处理器 P 和线程 M 的分离,当前线程 M 会陷入系统调用等待返回,当前线程上的锁被释放后,会有其他 Goroutine 抢占处理器资源。
// Standard syscall entry used by the go syscall library and normal cgo calls.
func entersyscall() {
// 获取当前程序计数器和栈位置调用 reentersyscall
reentersyscall(getcallerpc(), getcallersp())
}
//go:nosplit
func reentersyscall(pc, sp uintptr) {
_g_ := getg()
// Disable preemption because during this function g is in Gsyscall status,
// but can have inconsistent g->sched, do not let GC observe it.
_g_.m.locks++ // 系统调用禁止抢占 M,禁止线程上发生的抢占,防止出现内存不一致的问题
// Entersyscall 不能调用任何可能导致栈分裂/增长的函数。保证当前函数不会触发栈分裂或者增长;
_g_.stackguard0 = stackPreempt
_g_.throwsplit = true
// 保存当前的程序计数器 PC 和栈指针 SP 中的内容;
save(pc, sp)
_g_.syscallsp = sp
_g_.syscallpc = pc
casgstatus(_g_, _Grunning, _Gsyscall) // 将 Goroutine 的状态更新至 _Gsyscall
if _g_.syscallsp < _g_.stack.lo || _g_.stack.hi < _g_.syscallsp {
systemstack(func() {
print("entersyscall inconsistent ", hex(_g_.syscallsp), " [", hex(_g_.stack.lo), ",", hex(_g_.stack.hi), "]\n")
throw("entersyscall")
})
}
...
_g_.m.syscalltick = _g_.m.p.ptr().syscalltick
_g_.sysblocktraced = true
pp := _g_.m.p.ptr()
pp.m = 0 // 将 Goroutine 的处理器和线程暂时分离
_g_.m.oldp.set(pp)
_g_.m.p = 0
atomic.Store(&pp.status, _Psyscall) // 更新处理器的状态到 _Psyscall
if sched.gcwaiting != 0 {
systemstack(entersyscall_gcwait)
save(pc, sp)
}
_g_.m.locks-- // 释放当前线程上的锁
}
exitsyscall() 退出系统调用
系统调用结束后,调用 runtime.exitsyscall 退出系统调用,为当前 Goroutine 重新分配资源;
//go:nosplit
//go:nowritebarrierrec
//go:linkname exitsyscall
func exitsyscall() {
_g_ := getg()
_g_.m.locks++ // see comment in entersyscall
if getcallersp() > _g_.syscallsp {
throw("exitsyscall: syscall frame is no longer valid")
}
_g_.waitsince = 0
oldp := _g_.m.oldp.ptr()
_g_.m.oldp = 0
if exitsyscallfast(oldp) {
...
if sched.disable.user && !schedEnabled(_g_) {
// 调用 Gosched G 让出 处理器,从 _Grunning 变为 _Grunnable
Gosched()
}
return
}
_g_.sysexitticks = 0
...
_g_.m.locks--
// 切换至调度器的 Goroutine 即 g0 调用 exitsyscall0
mcall(exitsyscall0) // 没有拿到处理器 P,把 G 放入可运行队列, _Gsyscall 变为 _Grunnable
_g_.syscallsp = 0
_g_.m.p.ptr().syscalltick++
_g_.throwsplit = false
}
先调用 runtime.exitsyscallfast 方法,寻找有没有可用的处理器 P:
- 原处理器处于
_Psyscall状态,就会直接调用wirep将 Goroutine 与处理器进行关联; G 状态从_Gsyscall变为_Grunning,return true - 如果调度器中存在闲置的处理器,就会调用
acquirep函数使用闲置的处理器处理当前 Goroutine;G 状态从_Gsyscall变为_Grunning, return true - 其他情况 return false
如果没有找到 P 运行,即 runtime.exitsyscallfast 返回 false,就 通过 mcall(exitsyscall0) 在 g0 上执行:
-
通过
pidleget获取到闲置的处理器时就会调用runtime.acquirep和runtime.execute在该处理器上执行 Goroutine,G 状态从_Gsyscall变为_Grunning; -
在其它情况下,将当前 Goroutine 放到全局的运行队列中,等待调度器的调度,G 状态从
_Gsyscall变为_Grunnable;
并且无论上述哪种情况,都会调用 schedule 函数触发调度器的调度。
Gosched() 主动让出调度器
调用 runtime.Gosched 的 Goroutine 主动让出处理器,允许其他 Goroutine 运行。通过在 g0 上调用 runtime.goschedImpl 把 G 状态 从 _Grunning 改为 _Grunnable 并放入全局运行队列,调用 runtime.schedule 重启出发调度器。
// Gosched 让出处理器,允许其他goroutines运行。
// 该函数无法挂起 Goroutine,调度器会在自动调度当前 Goroutine:
func Gosched() {
checkTimeouts()
mcall(gosched_m)
}
// Gosched continuation on g0.
func gosched_m(gp *g) {
if trace.enabled {
traceGoSched()
}
goschedImpl(gp)
}
func goschedImpl(gp *g) {
status := readgstatus(gp)
if status&^_Gscan != _Grunning {
dumpgstatus(gp)
throw("bad g status")
}
casgstatus(gp, _Grunning, _Grunnable)
dropg()
lock(&sched.lock)
globrunqput(gp)
unlock(&sched.lock)
schedule()
}
LockOSThread()
runtime.LockOSThread 绑定 Goroutine 和 OS 线程。
当 Goroutine 完成了特定的操作之后,就会调用以下函数 runtime.UnlockOSThread 分离 Goroutine 和线程;
大部分情况下,都用不到这一对函数,不过使用 CGO 或者经常与操作系统打交道的可能会见到它们的身影。
reference
https://www.ardanlabs.com/blog/2018/08/scheduling-in-go-part1.html
https://docs.google.com/document/d/1TTj4T2JO42uD5ID9e89oa0sLKhJYD0Y_kqxDv3I3XMw/edit