栈管理代码
[TOC]
stackinit()
runtime.schedinit 用于栈道初始化,在程序启动阶段被 runtime.sechedinit 中调用,主要用于两个全局栈缓存对象 runtime.stackpool 和 runtime.stackLarge 初始化。
func stackinit() {
if _StackCacheSize&_PageMask != 0 {
throw("cache size must be a multiple of page size")
}
for i := range stackpool {
stackpool[i].item.span.init()
lockInit(&stackpool[i].item.mu, lockRankStackpool)
}
for i := range stackLarge.free {
stackLarge.free[i].init()
lockInit(&stackLarge.lock, lockRankStackLarge)
}
}
stackalloc() 栈分配
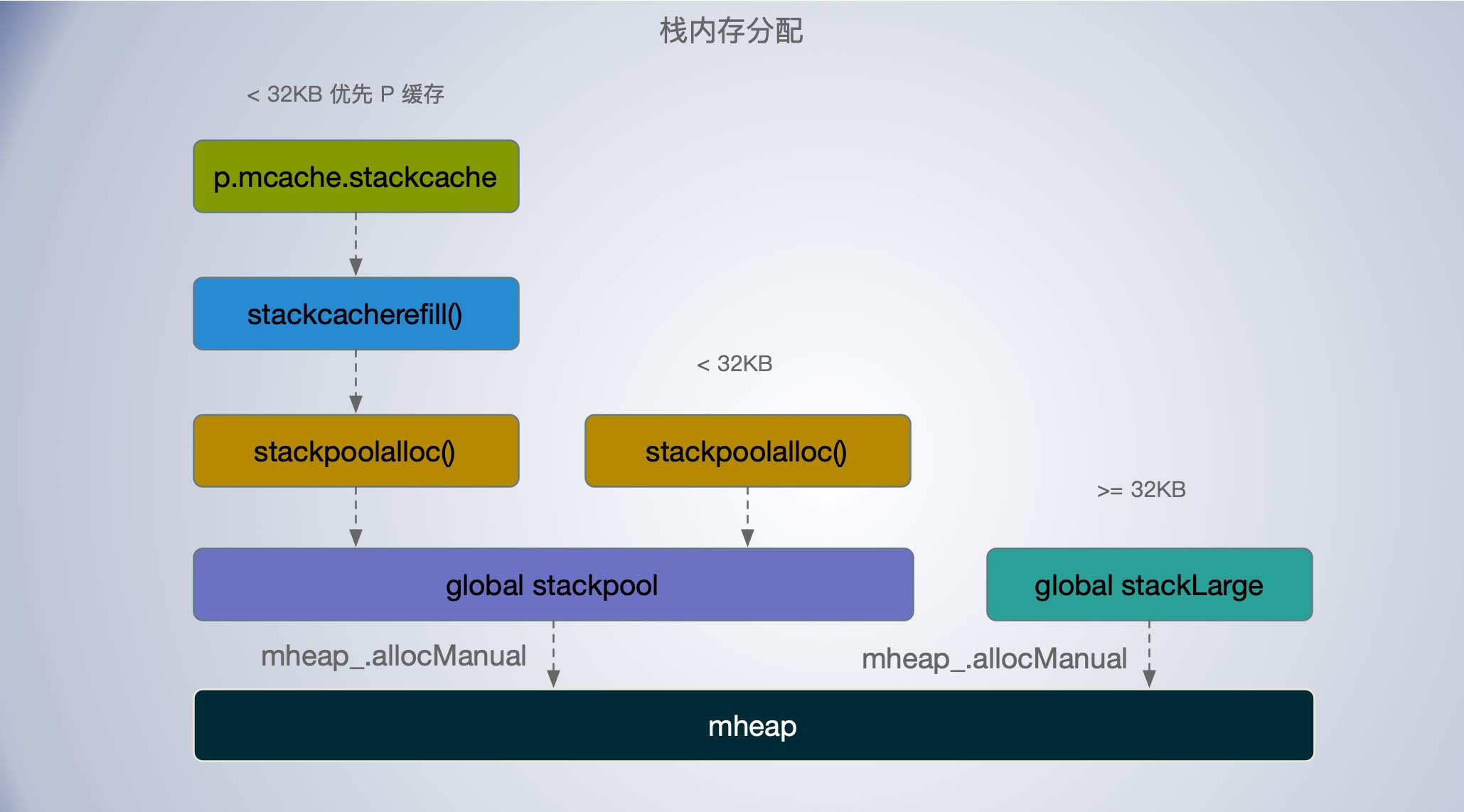
运行时会在 Goroutine 的初始化函数 runtime.malg 或者在 runtime.gfget 获取到 G 没有分配栈时会调用 runtime.stackalloc 分配一个指定大小的栈内存空间,根据线程缓存和申请栈的大小,该函数会通过三种不同的方法分配栈空间:
- 如果申请的栈空间小于 32KB,我们会在全局栈缓存池或者线程的栈缓存中初始化内存
- 如果Goroutine 没有分配处理器 P 或者 G 对应的OS线程暂时不可抢占,则调用
runtime.stackpoolalloc从全局缓存池分配栈内存; - 其他情况,分配小对象栈时,通过
runtime.stackcacherefill从线程缓存p.mcache中分配,如果线程缓存不足,也是调用runtime.stackpoolalloc从全局缓存池分配栈内存并缓存起来;
- 如果Goroutine 没有分配处理器 P 或者 G 对应的OS线程暂时不可抢占,则调用
- 如果申请的栈空间大于等于 32KB ,从全局的大栈缓存 runtime.stackLarge 中获取内存空间,若缓存不足,则如会调用
mheap_.allocManual从堆上申请一片的内存空间缓存起来;
从上面栈内存的分配策略来看,与堆内存分配有点相似,都用到了mspan 缓存; 为了减少锁开销,提高性能都分为了线程缓存(p.mcache.stackcache)和 全局缓存(stackpool 和 stackLarge),也根据大小进行了分类;
//go:systemstack
func stackalloc(n uint32) stack {
// Stackalloc必须在调度器(g0)栈上被调用,这样我们就不会在Stackalloc运行的代码中尝试增加堆栈。
// // 栈大小必须是2的指数倍
thisg := getg()
...
// Small stacks are allocated with a fixed-size free-list allocator.
// If we need a stack of a bigger size, we fall back on allocating
// a dedicated span.
var v unsafe.Pointer
// 申请的栈空间小于 32KB 时,在全局栈缓存池或者线程的栈缓存中初始化内存:
if n < _FixedStack<<_NumStackOrders && n < _StackCacheSize {
order := uint8(0)
n2 := n
for n2 > _FixedStack {
order++
n2 >>= 1
}
var x gclinkptr
if stackNoCache != 0 || thisg.m.p == 0 || thisg.m.preemptoff != "" {
// thisg.m.p == 0 可以发生在exitsycall或procresize的内部。只需从全局池中获取一个堆栈。
// 在gc期间不要碰 stackcache,因为它是并发刷新的。
lock(&stackpool[order].item.mu)
x = stackpoolalloc(order) // 在全局的栈缓存池 stackpool 中获取新的内存
unlock(&stackpool[order].item.mu)
} else {
c := thisg.m.p.ptr().mcache
x = c.stackcache[order].list
if x.ptr() == nil {
stackcacherefill(c, order) // 从堆上获取新的内存
x = c.stackcache[order].list // 从 mcache.stackcache 获取栈内存
}
c.stackcache[order].list = x.ptr().next
c.stackcache[order].size -= uintptr(n)
}
v = unsafe.Pointer(x)
} else {
var s *mspan
npage := uintptr(n) >> _PageShift
log2npage := stacklog2(npage)
// Try to get a stack from the large stack cache.
lock(&stackLarge.lock)
if !stackLarge.free[log2npage].isEmpty() {
s = stackLarge.free[log2npage].first
stackLarge.free[log2npage].remove(s)
}
unlock(&stackLarge.lock)
lockWithRankMayAcquire(&mheap_.lock, lockRankMheap)
if s == nil {
// Allocate a new stack from the heap.
s = mheap_.allocManual(npage, &memstats.stacks_inuse)
if s == nil {
throw("out of memory")
}
osStackAlloc(s)
s.elemsize = uintptr(n)
}
v = unsafe.Pointer(s.base())
}
if raceenabled {
racemalloc(v, uintptr(n))
}
if msanenabled {
msanmalloc(v, uintptr(n))
}
if stackDebug >= 1 {
print(" allocated ", v, "\n")
}
return stack{uintptr(v), uintptr(v) + uintptr(n)}
}
stackpoolallo()
从全局栈缓存池 runtime.stackpool 获取内存,如果栈缓存池中内存不足,会调用 mheap_.allocManual 从堆上申请一片 32KB 的内存空间;
然后在被用作栈内存之前,因为 OpenBSD 6.4+ 对栈内存有特殊的需求,所以只要我们从堆上申请栈内存,就需要调用 runtime.osStackAlloc 函数做一些额外的处理,然而其他的操作系统就没有这种限制了。
最后返回一块栈内存。
newstack()
调用 runtime.newstack 创建新的栈,替换旧栈,主要用来栈扩容和栈收缩。
在几函数调用之前运行 runtime.morestack,检查当前 Goroutine 的栈内存是否充足,如果当前栈需要扩容,会保存一些栈的相关信息,然后创建新的栈。
当 G 被设置可抢占时:
-
如果当前线程 M 为不可栈状态时,则直接调用 gogo(&gp.sched) 触发调取;
-
如果在
runtime.scanstack被标记为需要栈收缩,即gp.preemptShrink为 true,则调用runtime.shrinkstack进行栈收缩。 -
如果因在 GC 根标记
runtime.markroot期间, G 被runtime.suspendG挂起,则调用runtime.preemptPark被动让出当前处理器的控制权并将 Goroutine 的状态修改至_Gpreempted; -
其他则调用
runtime.gopreempt_m主动让出当前处理器的控制权, 解除与P,M 的关系,放入全局运行队列;
如果当前 Goroutine 未设置为可抢占,调用 runtime.copystack 申请一个为原来 2 倍的栈空间,调用 gogo(&gp.sched) 。
//go:nowritebarrierrec
func newstack() {
thisg := getg()
...
gp := thisg.m.curg
...
morebuf := thisg.m.morebuf
...
preempt := atomic.Loaduintptr(&gp.stackguard0) == stackPreempt
if preempt { // 如果当前的 G 可以被抢占,但是 G 对于的 M 不能抢占,则主动调用 gogo 出发调度
if !canPreemptM(thisg.m) {
gp.stackguard0 = gp.stack.lo + _StackGuard
gogo(&gp.sched) // never return
}
}
...
sp := gp.sched.sp
...
if sp < gp.stack.lo {
...
throw("runtime: split stack overflow")
}
if preempt { // 如果当前 G 可以抢占
if gp == thisg.m.g0 {
throw("runtime: preempt g0")
}
if thisg.m.p == 0 && thisg.m.locks == 0 {
throw("runtime: g is running but p is not")
}
// Goroutine 在垃圾回收被 runtime.scanstack 函数标记成了需要收缩栈
if gp.preemptShrink {
gp.preemptShrink = false
shrinkstack(gp)
}
// 如果当前 Goroutine 被 runtime.suspendG 函数挂起,
// 调用 runtime.preemptPark 被动让出当前处理器的控制权并将 Goroutine 的状态修改至 _Gpreempted
if gp.preemptStop {
preemptPark(gp) // never returns
}
// 主动让出当前处理器的控制权
gopreempt_m(gp) // never return
}
// 分配一个新栈,大小为原来的2倍
oldsize := gp.stack.hi - gp.stack.lo
newsize := oldsize * 2
if f := findfunc(gp.sched.pc); f.valid() {
max := uintptr(funcMaxSPDelta(f))
for newsize-oldsize < max+_StackGuard {
newsize *= 2
}
}
if newsize > maxstacksize {
...
throw("stack overflow")
}
casgstatus(gp, _Grunning, _Gcopystack) // 修改 G 状态
copystack(gp, newsize) // 就栈拷贝到新栈
if stackDebug >= 1 {
print("stack grow done\n")
}
casgstatus(gp, _Gcopystack, _Grunning)
gogo(&gp.sched)
}
在 newstack() 触发抢占调度
设置gp.preempt = true 表示可抢占信号。Goroutine 中的每次调用都通过将当前的栈指针与 gp->stackguard0 进行比较来检查堆栈溢出。将 P 的 stackguard0 设为 stackPreempt 导致该 P 中正在执行的 G 进行下一次函数调用时, 导致栈空间检查失败。进而触发 morestack(汇编代码实现),然后进行一连串的函数调用,最终会调用 goschedImpl 函数,进行解除 P 与当前 M 的关联,让该G进入 _Grunnable 状态,插入全局G列表 runq,等待下次调度。
触发的一系列函数如下: morestack() -> newstack() -> gopreempt_m() -> goschedImpl() -> schedule()
systemstack()
//go:noescape
func systemstack(fn func())
systemstack在系统堆栈上运行 fn。
如果systemstack从每个操作系统线程(g0)栈调用,或者如果 systemstack 从信号处理(gsignal)栈调用,则 systemstack 直接调用 fn 并返回。
否则,将从普通 goroutine 的有限栈调用 systemstack。在这种情况下,systemstack 切换到每个操作系统线程的栈,调用fn,然后切换回来。
通常使用函数字面值作为参数,以便与系统栈调用周围的代码共享输入和输出:
osStackAlloc()
在被用作栈内存之前,因为 OpenBSD 6.4+ 对栈内存有特殊的需求,所以只要我们从堆上申请栈内存,就需要调用 runtime.osStackAlloc 函数做一些额外的处理,然而其他的操作系统就没有这种限制了。
copystack() 用新栈替代旧栈
将 Goroutine 的栈拷贝到一个新的栈上,在栈扩容和栈收缩时会用到。
先调用 runtime.stackalloc 分配一个新的栈空间。
调用 runtime.memmove 将旧的栈拷贝到新的栈
调用 runtime.gentraceback 调整栈指针
调用 runtime.stackfree 释放旧的栈空间
shrinkstack() 栈对半收缩
与扩容不同,栈收缩不是在函数调用时发生的,是由垃圾回收器在 根标记期间执行 runtime.scanstack 扫描 Goroutine 栈内存时主动触发的。基本过程是计算当前使用的空间,小于栈空间的1/4的话, 执行栈的收缩,将栈收缩为现在的1/2。如果新栈的大小低于程序的最低限制 _FixedStack (linux 为2KB),那么缩容的过程就会停止。
func shrinkstack(gp *g) {
gstatus := readgstatus(gp)
...
// 收缩目标是一半大小
oldsize := gp.stackAlloc
newsize := oldsize / 2
// 栈最小不能小于 _FixedStack
if newsize < _FixedStack {
return
}
// 如果使用空间超过1/4, 则不收缩
avail := gp.stack.hi - gp.stack.lo
if used := gp.stack.hi - gp.sched.sp + _StackLimit; used >= avail/4 {
return
}
// 用较小的栈替换当前的栈
copystack(gp, newsize, false)
}
morestackc() 检查是否需要栈扩容
// Called during function prolog when more stack is needed.
//
// The traceback routines see morestack on a g0 as being
// the top of a stack (for example, morestack calling newstack
// calling the scheduler calling newm calling gc), so we must
// record an argument size. For that purpose, it has no arguments.
TEXT runtime·morestack(SB),NOSPLIT,$0-0
// Cannot grow scheduler stack (m->g0).
get_tls(CX)
MOVQ g(CX), BX
MOVQ g_m(BX), BX
MOVQ m_g0(BX), SI
CMPQ g(CX), SI
JNE 3(PC)
CALL runtime·badmorestackg0(SB)
CALL runtime·abort(SB)
// Cannot grow signal stack (m->gsignal).
MOVQ m_gsignal(BX), SI
CMPQ g(CX), SI
JNE 3(PC)
CALL runtime·badmorestackgsignal(SB)
CALL runtime·abort(SB)
// Called from f.
// Set m->morebuf to f's caller.
NOP SP // tell vet SP changed - stop checking offsets
MOVQ 8(SP), AX // f's caller's PC
MOVQ AX, (m_morebuf+gobuf_pc)(BX)
LEAQ 16(SP), AX // f's caller's SP
MOVQ AX, (m_morebuf+gobuf_sp)(BX)
get_tls(CX)
MOVQ g(CX), SI
MOVQ SI, (m_morebuf+gobuf_g)(BX)
// Set g->sched to context in f.
MOVQ 0(SP), AX // f's PC
MOVQ AX, (g_sched+gobuf_pc)(SI)
MOVQ SI, (g_sched+gobuf_g)(SI)
LEAQ 8(SP), AX // f's SP
MOVQ AX, (g_sched+gobuf_sp)(SI)
MOVQ BP, (g_sched+gobuf_bp)(SI)
MOVQ DX, (g_sched+gobuf_ctxt)(SI)
// Call newstack on m->g0's stack.
MOVQ m_g0(BX), BX
MOVQ BX, g(CX)
MOVQ (g_sched+gobuf_sp)(BX), SP
CALL runtime·newstack(SB)
CALL runtime·abort(SB) // crash if newstack returns
RET
freeStackSpans()
// Stack frame layout
//
// (x86)
// +------------------+
// | args from caller |
// +------------------+ <- frame->argp
// | return address |
// +------------------+
// | caller's BP (*) | (*) if framepointer_enabled && varp < sp
// +------------------+ <- frame->varp
// | locals |
// +------------------+
// | args to callee |
// +------------------+ <- frame->sp
//
// (arm)
// +------------------+
// | args from caller |
// +------------------+ <- frame->argp
// | caller's retaddr |
// +------------------+ <- frame->varp
// | locals |
// +------------------+
// | args to callee |
// +------------------+
// | return address |
// +------------------+ <- frame->sp